Similar to epidural injections, orthopedic injections are placed directly into the affected area to provide relief. The difference with orthopedic injections is that the high concentration of growth factors also helps with the healing process. Initially popular among professional athletes, orthopedic injections are being increasingly used by other patients looking to better manage pain from sudden (acute) injuries or chronic pain relegated to a specific area.
What are Orthopedic Injections?
In addition to helping with the clotting process, these concentrated injections contain hundreds of growth factors. These are a special group of proteins that stimulate the growth and repair of tissues.
Orthopedic injections can include as much as 5-10 times as many growth factors than what’s normally in blood. It’s believed that injections that are “richer” in growth factors facilitate the healing process.
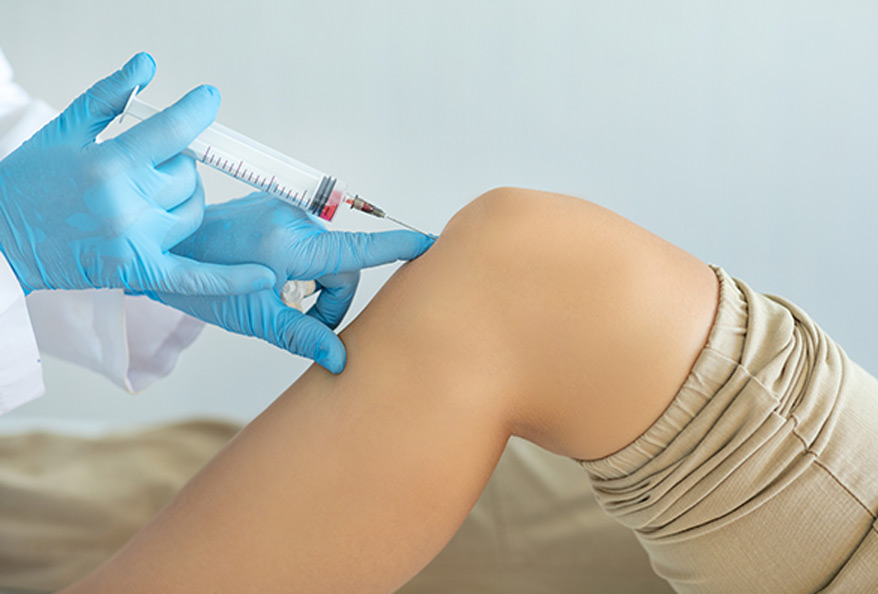
How Do the Injections Work?
Orthopedic injections are prepared from a patient’s own blood, so there is no risk of transmissible infection. The blood is centrifuged (spun and separated) to produce a mixture that has a greater concentration of growth factors. Combined with a local anesthetic to ease any discomfort from the shot, the injection is placed directly into the affected area.
Injections of growth factors speed up the healing process by initiating tissue repair and attracting specialized cells (undefined cells) that repair damaged cells in tissues. If injections need to be repeated, the general recommendation is no more than three injections per six-month period.
What Can Be Expected After Receiving an Injection?
Post-injection imaging tests have confirmed that improved tissue healing does take place after these injections. It usually takes a few weeks to see noticeable results as the healing process continues. Patients sometimes experience lasting relief if tissues completely heal. With chronic conditions, the injections may make it easier to manage pain without surgery.
When Should Injections Be Considered?
Before orthopedic injections are considered, a likely source of pain needs to be clearly identified. Even then, injections are usually recommended if other forms of pain management such as hot and cold therapy, physical therapy, and the use of anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving medications aren’t effective.
Factors that usually determine if orthopedic injections will likely be effective include the location of the injury and the patient’s overall health. Orthopedic injections may be used to ease pain related to a growing number of conditions.


